Gross Income vs Net Income: The Differences, Explained

If you reported wages in Box 16, then Box 17 will show the amount of state taxes withheld from you and your employee’s income. If you live in a state with a flat state tax, it’s good to double-check withholdings by multiplying the amount in Box 16 by that state’s tax rate. Medicare wages and tips are the total amount of earnings you make that are subject to Medicare tax. These taxes don’t usually subtract pre-tax deductions and include taxable benefits like bonuses and vacation. There also isn’t a cap on Medicare taxes, which means the number in Box 5 can be significantly larger than what’s shown in Box 1 or Box 3.

How to calculate gross income
- Offer health, dental, vision and more to recruit & retain employees.
- If you also work 10 hours of overtime, your gross pay would increase to $2,750.
- Beyond that, net income is the most widely used measure of a business’s success, while gross income offers insight into the efficiency of a business’s operations.
- In some cases, companies expect losses over the first months or even years of operating due to high start-up or overhead costs.
- Net profit margin, or net margin, is the ratio of net profits to revenues.
Business expenses, including office rent ($12,000), software subscriptions ($3,000), travel ($5,000), and marketing ($10,000), total $30,000. Understand the key differences between gross and net income, how deductions unearned revenue impact earnings, and see practical examples for employment, business, and investments. Overhead—such as rent, utilities, payroll, marketing and advertising, and business insurance—isn’t directly tied to producing goods or services. These generally don’t change very much based on a company’s output and sometimes they’re referred to as fixed costs. The cost of goods sold includes only expenses directly tied to the production of a company’s goods or services, such as raw materials, shipping, and labor.

Financial Goals
Both figures provide valuable clues about your operation for investors, lenders, and potential business partners. Savvy business owners also track gross and net income to spot trends, pivot strategies, and ensure sustainable cash flow. Net income is the total amount of money that your company earned in a period less all business expenses.
Gross Income vs Net: Key Differences and Examples Explained
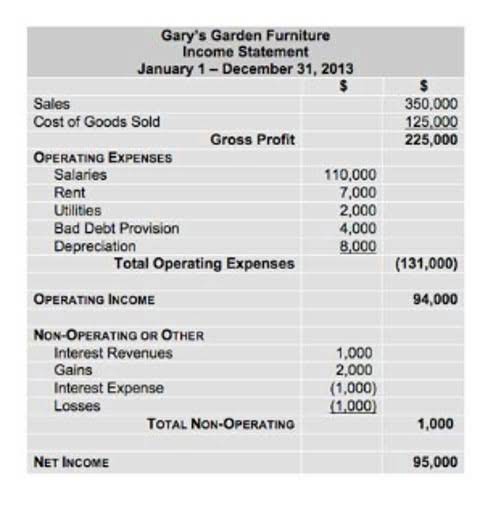
You need to know if every sale you make is profitable or if overhead is smothering your healthy sales. Running these calculations can help stakeholders in Greenlight Apples understand more about the financial health of their business and any levers they can pull to increase profits. To calculate the net income or profit for Greenlight Apples, we subtract total expenses from total income. Knowing the revenue ($1,000,000) and COGS ($250,000), we can calculate that the gross profit for Greenlight Apples is $750,000. Net HVAC Bookkeeping profit margin, or net margin, is the ratio of net profits to revenues.
- This is the total money you’ve earned from working, investing and any other source of revenue before taxes.
- By looking at your various revenue streams, you can see which clients and which types of projects bring in the most income and the least income.
- By knowing what deductions are taken out of your gross income, you can better understand your net income and plan your finances accordingly.
- Individual gross income also can include income from pensions, annuities, investment gains and dividends, and rental income.
- Net income, however, is the disposable income available after all expenses.
Understanding the difference between gross income and net income is essential for managing personal finances, running a business, or evaluating investments. These two figures play a key role in budgeting, tax planning, and financial decision-making, yet they are often confused. Net income, or net profit, is what a business has left after subtracting all of its expenses from revenue.

A Guide to Nonprofit Accounting (for Non-Accountants)
A typical example can range from auto expenses to entertaining clients and from participating in trade shows to paying local business taxes and fees. To start, I’m in a very low tax bracket so I know I’m not losing a ton of money to taxes. Any taxes withheld on the wages in Box 18 get reported in Box 19.
Time and Attendance
The primary difference between gross and net income lies in deductions. Gross income is your total earnings before any deductions, while net income is what remains after all deductions are applied. This distinction is crucial for evaluating your financial health and making informed budgeting decisions.
Imagine you sign a contract stating you will earn $60,000 a year. It’s the amount that gets reported to the tax authorities and forms why is net income lower than gross income the basis of your financial health assessment. However, it’s not the amount you’ll actually see in your bank account because various deductions will take a bite out of this total. Contributions to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-deductible, with 2024 limits set at $4,150 for individuals and $8,300 for families. Those with high-deductible health plans can use HSAs to cover medical expenses while reducing taxable income. Similarly, self-employed individuals can deduct health insurance premiums.




